You often face temperature control PCBA failure due to three critical thermal management design defects. These issues include inadequate material selection, poor heat dissipation design, and flawed component placement and layout. High product return rates demand immediate action. Identifying and fixing these defects improves thermal performance, reduces heat stress, and enhances PCB reliability.
PCBA Heat Dissipation Guide: Essential Strategies to Prevent Hot Spots and Component Failure
- Choose materials with high thermal conductivity, like aluminium or ceramic, to improve heat dissipation and reduce failure risks.
- Optimise component placement to avoid hot spots. Position heat-generating parts away from sensitive components to enhance thermal performance.
- Implement effective heat dissipation solutions, such as heatsinks and thermal vias, to manage excess heat and extend product life.
- Use thermal analysis tools during the design phase to identify potential hot spots and validate your PCB layout for better reliability.
- Follow industry standards and best practices in thermal management to ensure safety, performance, and lower product return rates.
PCBA Material Selection and Thermal Failure
Material Impact on PCBA Temperature
You must understand how material choices directly affect temperature control and thermal performance in printed circuit boards. The thermal conductivity of PCB substrates determines how efficiently heat dissipates from components. For high-temperature environments, selecting materials with superior heat dissipation is essential for reliability and performance. Consider the following comparison of common PCB materials and their thermal properties:
| Material Type | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
|---|---|
| FR-4 | 0.3 – 0.5 |
| Alumina-based DBC | 24 – 30 |
| Aluminium Nitride DBC | Up to 180 |
Ceramic substrates and metal-core PCBs offer much higher thermal conductivity than standard FR-4, making them ideal for effective thermal management in demanding applications. When you use these materials, you improve heat dissipation and reduce the risk of temperature-controlled PCBA failure.
Common Material Selection Errors
You often encounter failures in PCB thermal design due to mismatches in the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) between layers. These mismatches create thermal stress, leading to solder joint fatigue and delamination. Hard solder materials can worsen thermal stresses, causing solder joint degradation. Inappropriate conformal coatings may also increase fatigue, especially if you ignore CTE and coating thickness. Common failure modes include:
- Delamination between interfaces from residual thermal stress
- Die cracking due to repeated thermal cycling
- Metal layer displacement from heat-induced deformation
Note: High product return rates often trace back to these material-related failures. You must address them early in the design phase to maintain reliability.
Preventing Material-Related Failures
You can prevent temperature-controlled PCBA failure by following best practices in thermal management design. Start by choosing substrates with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminium-backed or ceramic PCBs, for high-temperature PCB applications. Use thicker copper layers and thermal vias to enhance heat dissipation. Optimise component placement to minimise heat concentration and improve overall thermal performance. Integrate cooling elements like heat sinks or fans, and design enclosures to avoid trapping heat. Always validate your PCB thermal management with thermal analysis and simulation tools. Adhering to industry standards like IPC, RoHS, and UL certification ensures your materials meet safety and environmental requirements. By applying these thermal management techniques, you reduce the risk of failure and improve the reliability and performance of your printed circuit boards.
Thermal Management Design and Heat Dissipation
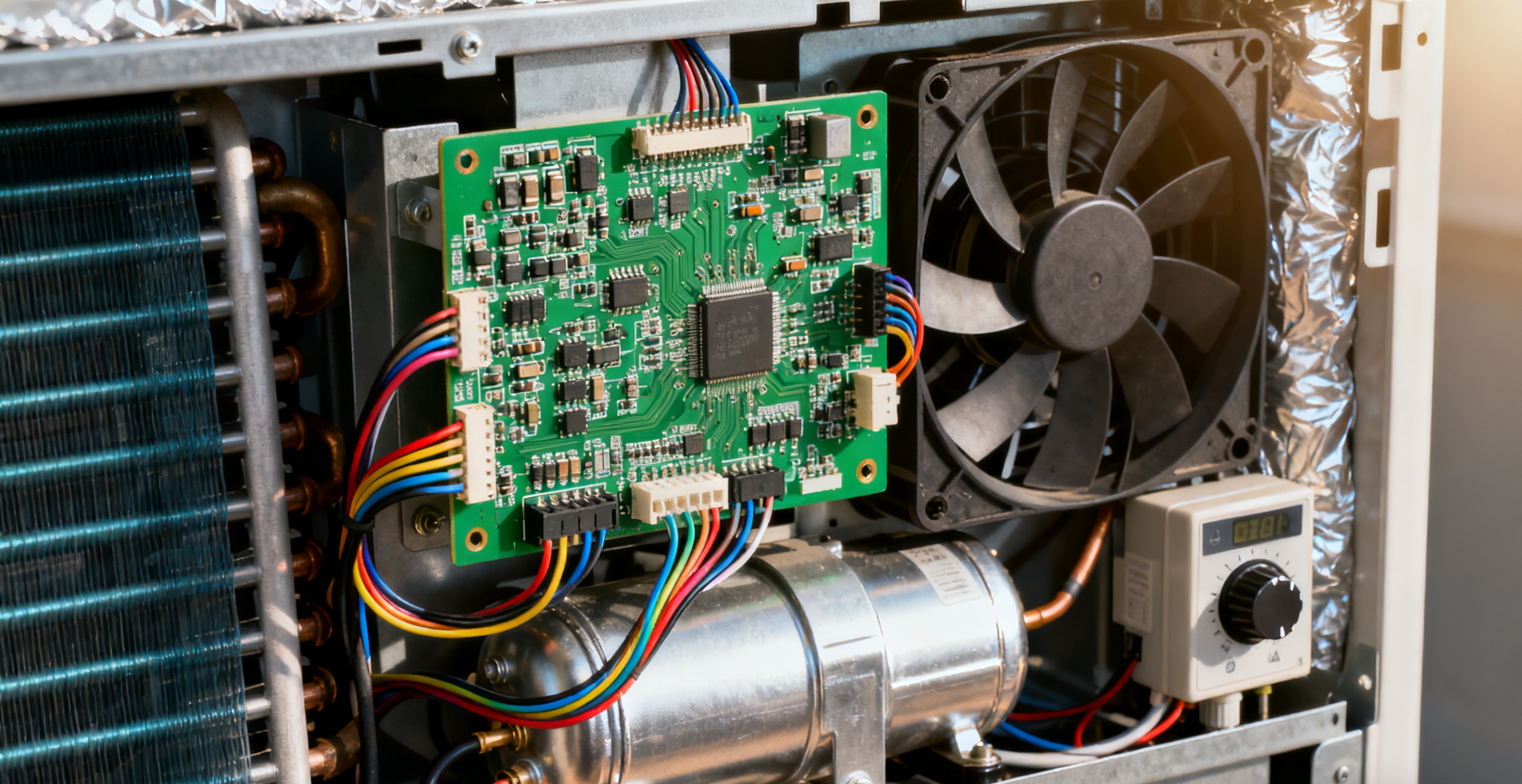
Heat Dissipation in PCBA Design
You must prioritise thermal management design to ensure the reliability and performance of your PCBA products. Effective heat dissipation prevents temperature spikes that can damage components and shorten the lifespan of printed circuit boards. When you implement proper thermal strategies, you reduce the risk of temperature control PCBA failure and lower product return rates. The following table summarises how thermal management impacts reliability and performance:
| Impact of Thermal Management on PCBA Products | Description |
|---|---|
| Component Failures | Reduces the risk of failures and thermal stress, enhancing reliability. |
| Performance Optimization | Maintains stable operation and improves overall performance. |
| Warranty Claims | Minimises overheating issues, leading to fewer returns and repairs. |
You should always consider factors such as circuit layout, power input, and device characteristics. These influence heat generation and dissipation in high-temperature environments.
Typical Thermal Design Flaws
Many temperature control PCBA failures stem from common mistakes in pcba thermal design. You might overlook the need for adequate heatsinks or use thin copper layers, which trap heat and create hotspots. Poor component placement can block airflow, causing the temperature to rise above safe limits. Other frequent errors include:
- Insufficient thermal vias prevent efficient heat escape.
- Inadequate copper planes, leading to uneven temperature distribution.
- Overloaded components, which generate excessive heat and risk failure.
- Blocked airflow paths, especially in densely packed pcba assemblies.
These flaws can accelerate device ageing, cause warping, and result in soldering defects. You must address these issues early in the design process to maintain high thermal performance and reduce costly returns.
PCB Heat Dissipation Solutions
You can improve pcba thermal design by applying proven PCB heat dissipation solutions. Start by using thick copper traces, which lower thermal resistance and distribute heat more evenly. Add thermal via arrays near heat sources to enhance conduction. Integrate cooling mechanisms such as heatsinks, heat pipes, or fans to remove excess heat from high-temperature pcba assemblies. The table below outlines effective solutions:
| Solution | Description |
|---|---|
| Heat Sinks | Conduct heat away from components, improving overall thermal performance. |
| Heat Pipes | Transfer heat efficiently in compact devices, supporting stable temperature control. |
| Cooling Fans | Remove hot air, preventing heat buildup in power-dense pcba designs. |
| Thermal Via Arrays | Enhance heat conduction, especially when placed close to heat-generating components. |
| Thick Copper Traces | Increase surface area for heat dissipation, ideal for high-power applications. |
You should also use thermal analysis tools during the design phase. These tools help you visualise temperature distribution and optimise your thermal management design. Following a thermal design guide ensures you select the right materials and layout for your application. By adopting these strategies, you boost reliability, extend product life, and address the root causes of temperature control PCBA failure.
Component Placement, Layout, and Temperature Issues

Layout Effects on Thermal Performance
You must pay close attention to component placement and routing in your pcba thermal design. Poor layout can create temperature hot spots, which threaten the reliability and performance of your printed circuit boards. When you position heat-generating components like power regulators or CPUs too close together, you increase the risk of excessive heat buildup. High-density placements restrict airflow, making it difficult for cooling solutions to work effectively. Tracks carrying high currents also generate heat, and narrow traces can worsen the problem. Wider traces and strategic routing help improve heat dissipation and thermal performance. Effective thermal management design starts with balancing power distribution and ensuring adequate spacing for airflow.
- Components that generate significant heat can reach temperatures above 100°C.
- Inadequate spacing for airflow leads to heat accumulation and temperature control issues.
- Closely placed components risk damage to nearby parts and compromise board integrity.
Hot Spots and Failure Risks
Temperature hot spots in your pcba can cause serious failure risks. High temperatures degrade materials, leading to delamination and structural failure. Components may drift outside their specified performance ranges, resulting in unpredictable behaviour or outright failure. Mechanical stresses from different thermal expansion rates can fatigue solder joints and crack components. Excessive heat can also damage circuit lines and cause oxidation, further reducing reliability. In high-temperature environments, these risks become even more pronounced, increasing product return rates and highlighting the urgency of robust thermal management.
- Material degradation and delamination
- Component performance drift and unpredictable operation
- Solder joint fatigue and cracking
Optimizing Placement for Thermal Control
You can minimise temperature control PCBA failure by following proven layout strategies. Start by identifying heat-generating components and placing them near board edges for better access to ambient air. Avoid positioning heat-sensitive components near hot zones. Use copper planes and thermal vias to spread and dissipate heat efficiently. Evenly distribute power-hungry components across the pcba to prevent localised hot spots. Align component placement with airflow paths to enhance cooling and overall thermal performance. Consider enclosure design to accommodate heatsinks and other PCB heat dissipation solutions.
| Guideline | Description |
|---|---|
| Strategic Placement of Heat-Generating Components | Position heat-generating components in areas with optimal airflow to enhance heat dissipation and avoid interference with sensitive components. |
| Even Distribution of Power Components | Spread power-hungry components evenly across the PCB to prevent thermal hotspots and ensure balanced thermal performance. |
| Use of Thermal Vias and Copper Planes | Place heat-producing components near thermal vias to facilitate heat transfer and use copper planes for efficient heat distribution. |
| Avoid Heat-Sensitive Components Near Hot Zones | Ensure heat-sensitive components are distanced from heat-generating areas to maintain their performance and longevity. |
| Position Components for Optimal Airflow | Align component placement with airflow paths to enhance cooling and reduce thermal build-up. |
| Isolate High-Power and Low-Power Components | Keep high-power components separate from low-power components to minimise thermal interference. |
| Consider Enclosure Design | Design the enclosure to accommodate heatsinks and cooling solutions, ensuring effective thermal management. |
You should use thermal analysis tools and follow a thermal design guide to validate your pcba layout. By optimising placement and routing, you improve thermal conductivity, control heat dissipation, and boost reliability. These strategies address the root causes of temperature control PCBA failure and help reduce costly product returns.
You face frequent temperature control PCBA failure when you overlook material selection, heat dissipation, and component placement in your PCB design. These defects can cause overheating, delamination, solder joint failure, and signal integrity issues. Reviewing your PCB for thermal management design flaws helps you reduce product returns and improve performance. When you upgrade materials, optimise layout, and use PCB heat dissipation solutions, you achieve lower peak temperatures and pass compliance tests. Apply these strategies to boost reliability and address the root causes of temperature control PCBA failure.
- Overheating leads to premature failure and degraded performance.
- Poor heat dissipation affects soldering quality and increases the risk of delamination.
- Improper component placement creates hotspots and signal faults.
Tip: Use thermal analysis tools and validate your PCB layout to ensure effective heat management.
FAQ
What causes frequent temperature control PCBA failure?
You often see failures from poor material selection, weak thermal management design, or incorrect component placement. These issues create hot spots and stress, which increase product return rates. You must address these root causes early to improve reliability.
How does thermal management design impact PCBA reliability?
You improve reliability when you manage heat flow efficiently. Good thermal management design prevents overheating, reduces stress on components, and extends product life. You lower the risk of costly failures and returns by focusing on heat control.
What is a PCB heat dissipation solution?
A PCB heat dissipation solution uses methods like heat sinks, thermal vias, and copper planes to remove excess heat. You keep components within safe temperature limits and avoid performance drops or failures by applying these solutions.
How can I reduce product return rates due to overheating?
You should review your design for material quality, heat dissipation, and component layout. Use simulation tools to spot hot spots. Apply proven PCB heat dissipation solutions to control temperature and boost customer satisfaction.
When should I use advanced materials for PCBA?
You should choose advanced materials for high-power or high-temperature applications. These materials offer better heat transfer and durability. You prevent temperature control PCBA failure and reduce returns by selecting the right substrate.